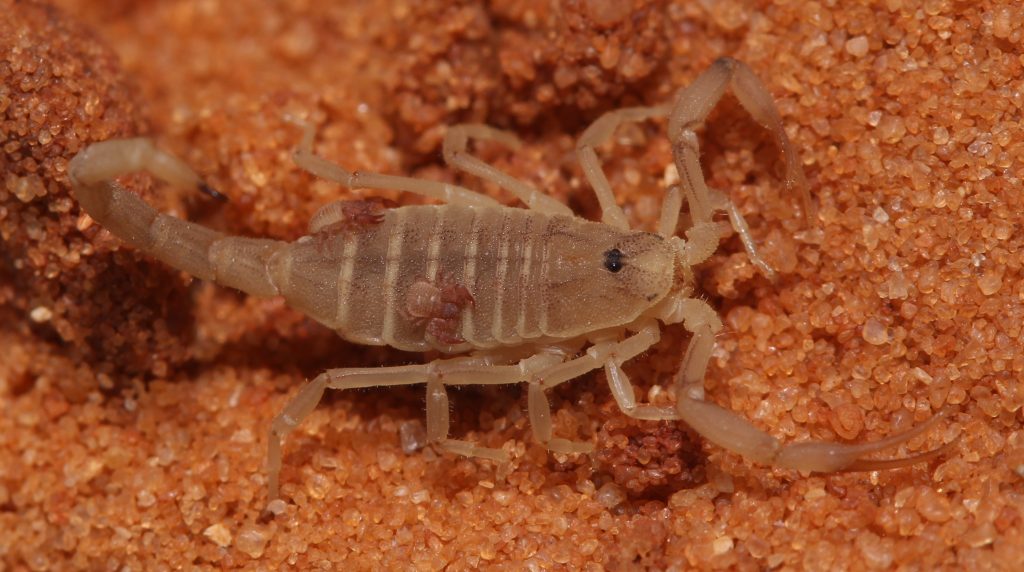
March 18, 2024 — A recent study led by Dr. Sharon Warburg and Dr. Efrat Gavish-Regev from the National Natural History Collections at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem (HU) alongside University of Haifa Ph.D. student Yoram Zvik, documented the first observation of phoresy (a phenomenon where one animal attaches to a host to be taken to new environments) with a pseudoscorpion on a scorpion. The pseudoscorpion Nannowithius wahrmani was observed clinging onto the scorpion Birulatus israelensis. Documented instances of phoresy have been seen in mammals, birds, insects, and even other arachnids.
Nannowithius wahrmani, part of the Withiidae family of pseudoscorpions, encompasses 37 genera and 170 species that can be found all over the world, with a significant presence in tropical and subtropical regions. It was also observed that species within the genus Nannowithius exhibit myrmecophilous tendencies (having positive interspecies associations with ants), often forming a mutually beneficial relationship with ant colonies.

The study conducted was part of an extensive seven-year study, involving field surveys, nest monitoring, and observations in the eastern part of Israel. Over a thousand observations of Birulatus israelensis were documented, with only two observations of the pseudoscorpions species Nannowithius wahrmani on the scorpion’s back during specific dates in late spring.
This groundbreaking observation not only expands our understanding of arachnid behavior but also opens avenues for future research into the intricate world of symbiotic relationships within the ant nest ecosystem. It also prompts further exploration into how pseudoscorpions elude ants, their alternative hosts, and how the arachnids decide to disperse (how they decide to expand the locations in which they live).
The research paper titled “Hitching a ride on a scorpion: the first record of phoresy of a myrmecophile pseudoscorpion on a myrmecophile scorpion” is now available in BioOne Complete and can be accessed here.
Researchers:
Sharon Warburg1, Yoram Zvik2,3, Efrat Gavish-Regev1
Institutions:
1) The National Natural History Collections, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Edmond J. Safra Campus, Givat Ram, Jerusalem
2) Hoopoe Ornithology & Ecology Center, Yeroham
3) Department of Evolutionary and Environmental Biology, University of Haifa, Haifa
Related articles
Hebrew University-Hadassah School of Dental Medicine Establishes the Robert I. Schattner Oral Health Center for People with Disabilities
December 15, 2025 – The Hebrew University-Hadassah School of Dental Medicine is proud to announce the establishment of the Robert I. Schattner Center for Oral Health for People with Disabilities, an innovative center dedicated to providing quality dental care for people with physical,
New System That Exponentially Speeds Carbon Capture Could Help Slow the Rate of Global Warming
December 15, 2025 – Compressing thousands of years into hours, researchers at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem (HU) have, for the first time, created a lab “machine” to capture carbon dioxide, accelerating a natural process. A new paper published in Environmental Science &
New “Molecular Ruler” Tracks Growth of Alzheimer’s-Linked Tau Fibrils
December 15, 2025 – A team of chemists and biochemists developed a powerful new method to measure the size of protein clumps linked to Alzheimer’s and related dementias in tiny fluid samples, without the need for a microscope slide. The technology, called FibrilPaint and